|
Who is a Rheumatologist
A Rheumatologist is a qualified physician, with an additional training and experience in the diagnosis and treatment of arthritis and related musculoskeletal conditions.
What is arthritis?
Arthritis means inflammation (pain, swelling) of the joint.
How do you know whether you have arthritis?
Arthritis patients will experience the following symptoms: pain and swelling of one or more joints, feel stiffness in the joints – more in the morning, redness and warmth of the affected joints, recurring pain and tenderness in the joints.
Is it seen only in elderly people?
No, that is a misconception. Arthritis can affect any age group. But osteoarthritis (wear and tear arthritis) usually affects old people but can occur earlier in people with history of joint injuries & in those with hypermobile joints & obesity.
Is arthritis more common in women?
Yes, arthritis generally is more common in women than men. Rheumatoid arthritis is 3 times more common in women. However, Ankylosing spondylitis presenting with severe early morning stiffness is found more commonly in male population.
What is osteoarthritis?
It is a wear and tear arthritis affecting mainly weight bearing joints( e g Knee) seen in old people but can occur earlier in people with history of joint injuries & in those with hypermobile joints & obesity.
What is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
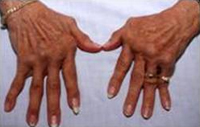
Rheumatoid Arthritis is an autoimmune disease that mostly affects joints. It is generally a chronic disease that if left untreated can lead to significant pain, disability, and deformities.
Do you recommend any special diet for arthritis?
No special diet is required for arthritis patients except Gout where low purine diet and limiting the alcohol are important. In patients who are obese, reduction of weight with low calory diet is advisable.
Will exercise help my joints?
Yes, it helps to reduce the pain and stiffness in the joints. Exercise also helps in increasing the flexibility, range of movement and strengthening the muscles around the joint. However, patients with deformities of the joints, should consult a Rheumatologist about the type of exercise.
How can a Rheumatologist help you?
A Rheumatologist helps in
- Making the correct diagnosis
- In treating the condition
- In recognizing the complications at an early stage
- In preventing further joint damage, joint deformities and joint contractures and ultimately improving the quality of life.
What are your business hours?
Our practice hours are from 8:30am to 5:30pm, Monday through Friday. Appointments can be made by telephoning our practice at 056-7775146.
What should I bring with me when I come for an appointment?
When you come for your appointment remember to bring the following:
- Insurance information
- Referral Letter form Gp or referring Doctor (if required)
- Copies of results, Blood tests, x-rays, MRI's. CT scans etc and any other relevant information
- List of medications (if any)
What is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Rheumatoid Arthritis, also called RA, is an autoimmune disease that mostly affects joints. It is generally a chronic disease that if left untreated can lead to significant pain, disability, and deformities.
Who gets RA?
About one percent of people worldwide have rheumatoid arthritis. It is twice as common in women as men. Often, RA starts in women in their childbearing years. However, it can affect anyone at any age.
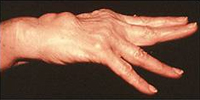
What are the symptoms of RA?
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis develop pain, swelling, and stiffness in their joints. The symptoms may start abruptly or occur gradually over time. Some patients will have many joints which are swollen and painful, while others may have just a few joints involved. Most patients will have stiffness when they first wake up that persists for 30 minutes or more. RA generally involves both sides of the body and often involves the small joints of the hands and wrists as well as the feet. Additionally, the elbows, shoulders, hips, knees, and ankles can be affected.
What are the advantages of being seen early?
Studies have shown that patients diagnosed and treated early have better long-term outcomes. There is growing evidence that early therapeutic intervention in the course of Inflammatory Arthritis like rheumatoid arthritis or psoriatic arthritis leads to earlier disease control and less joint damage. Additionally, in the short term they are able to have better relief of their pain and return to work and their other daily activities faster.
How do I know if I should be evaluated for RA?
Patients with warm, stiff, swollen joints, especially the hands and feet, that persist for four weeks should see their physician and ask if they might have symptoms of RA.
What happens at the rheumatology clinic in my evaluation for rheumatoid arthritis?
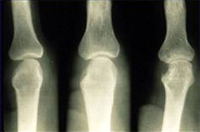
The first step in evaluation is talking about your symptoms and then undergoing a physical examination to look for red, warm, or swollen joints. X-rays of your hands and feet will be taken to look for any damage that may have occurred from inflammation. Recently there evidence supporting the use of Ultrasound scans or MRI scans showing additional benefit in diagnosis of earlier joint damage and inflammation. Also, blood tests will be done to look for markers of inflammation (Sedimentation rate or C-reactive protein) or antibodies related to rheumatoid arthritis (Rheumatoid Factor or anti-CCP antibodies). Your primary care doctor may or may not have done some X-rays or blood work in evaluating your symptoms.
How long does it take to find out the results of my tests and start on treatment?
It takes about one week for results of your blood work to return. Depending on your symptoms, their severity, and the findings on your physical exam, some treatment may be started at your initial visit. Our goal is start patients on treatment within 15 days of diagnosis of RA as this leads to better outcomes long-term.
What is the treatment for RA?
There are numerous medications available for RA. In the short term, many patients are started on ibuprofen or related medicines to decrease the pain and swelling. Patients who present with moderate to severe symptoms are often started on prednisone to decrease their swelling and pain. The long term treatment of RA requires treatment with one or more medications called DMARDs (Disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs). These include medications such as hydroxychloroquine, methotrexate, leflunomide, or sulfasalazine and Biologics( Injection treatment).
Your doctor can help tailor your treatment based on your symptoms, other medical conditions and medications, and the potential side effects of the medication. Additionally, we will be in communication with your primary care provider about your diagnosis and plan of treatment.
I think I may have RA, what is my next step?
If you think your symptoms may be RA, then schedule an appointment with your primary care physician or Gp to discuss them. They can refer you to see a rheumatologist for a comprehensive evaluation. If your symptoms have started between the last four weeks to six months, then your provider may consider sending you to our Early Arthritis Clinic.
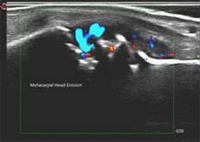
What is Musculoskeletal Ultrasound and its use in Rheumatology and Pain Management?
Musculoskeletal ultrasound is rapidly emerging as valuable diagnostic tool for Rheumatologists. It improves clinical diagnosis as well as interventional skills and aids in the screening and diagnosis of arthritis.
Procedure:
Ultrasound scanning is noninvasive (no needles or injections) and totally painless. The procedure takes less than 20 minutes. Warm gel is placed on the area of the body to be examined. The ultrasound probe is moved around to obtain specific images of the joints, muscle, tendon or soft tissue to be examined such as tears of the rotator cuff or the Achilles tendon in the ankle, joint damage or erosions seen in rheumatoid and inflammatory arthritis, fluid collections within joints like Osteoarthritis knees, tendonopathy, muscle pains and bursitis can also be examined and diagnosed.
Typical indications for ultrasonography in Rheumatology include:
A wide spectrum of pathologic conditions of the musculoskeletal system can be demonstrated:
- Muscles, Tendons, Ligaments
- Superficial Joints
- Shoulder Pain
- Shoulder Tendon Tears (Rotator Cuff)
- Soft tissue Swellings and Bumps
- Foreign Bodies
- Bursitis
- Impingement
For appointments Click here
|